Digital advertising has become a critical component of marketing strategies for businesses of all sizes. In an age where technology dominates our daily lives, the significance of effectively reaching and engaging consumers through digital channels cannot be understated. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of digital advertising, exploring its characteristics, various types, pricing models, performance metrics, best practices, common pitfalls, and recent trends in the field.
1. What is digital advertising?
At its core, digital advertising refers to the promotion of products or services through digital mediums. It encompasses a wide range of platforms and formats designed to reach potential customers across various online and offline environments. Digital ads can manifest as text, images, videos, and even interactive content, making them versatile tools for marketers looking to capture consumer attention.
As part of the broader digital marketing ecosystem, digital advertising includes any promotional activity conducted via electronic devices. This means ads can appear not only on websites and social media platforms but also on mobile applications, smart televisions, and online streaming services. The landscape is continuously evolving, characterized by rapid technological advancements that reshape how businesses connect with their audiences.
2. The Importance of Digital Advertising in Today’s Market
The transition from traditional advertising methods to digital is not merely a trend; it reflects changing consumer behaviors and preferences. Today’s consumers are more connected than ever, spending significant time on their devices. Consequently, businesses must adapt their marketing strategies to align with these new realities.
Digital advertising offers several advantages over traditional methods. It provides greater reach, allowing brands to target specific demographics and interests, and enables real-time data analysis for ongoing campaign optimization. Moreover, digital ads tend to be more cost-effective, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises that may lack the substantial budgets typically associated with legacy advertising channels.
3. Characteristics of Digital Advertising
Understanding the fundamental characteristics of digital advertising helps businesses appreciate its unique advantages and challenges.
- Paid Media Framework
Digital advertising typically operates within a paid media framework. Advertisers invest in purchasing space or visibility for their ads across various digital platforms, similar to traditional advertising models. However, the difference lies in the granularity of targeting and measurement capabilities available in the digital realm.
This investment allows businesses to reach vast audiences quickly. Unlike organic marketing efforts, which may take time to build momentum, paid digital ads can generate immediate traffic and brand exposure. Advertisers can choose from numerous options, including pay-per-click (PPC), cost-per-thousand impressions (CPM), and other models tailored to their goals.
- Measurability and Analytics
One of the most significant advantages of digital advertising is its measurability. Advertisers can track and analyze multiple performance metrics, allowing them to understand how their campaigns are performing in real-time. Metrics such as clicks, impressions, engagement rates, and conversion rates provide insights into the effectiveness of ad placements and messaging.
Advanced analytics tools enable businesses to refine their strategies based on concrete data rather than assumptions. For instance, if a particular ad format isn't driving the desired results, adjustments can be made almost instantaneously, leading to better resource allocation and improved ROI.
- Target-Oriented Approach
Digital advertising thrives on precision targeting. Advertisers can tailor their messages to specific audience segments based on demographic information, interests, behaviors, and contextual factors. This level of segmentation ensures that ads reach the most relevant consumers, increasing the likelihood of engagement and conversion.
Furthermore, the rise of retargeting strategies allows brands to reconnect with users who have previously interacted with their content. By serving ads to this audience, businesses can capitalize on prior interest, gently nudging potential customers closer to making a purchase decision.
- Personalization Capabilities
Personalization is at the heart of successful digital advertising. With access to vast amounts of data about consumer behavior, advertisers can craft customized messages that resonate with individuals. This might involve using dynamic content that changes based on user preferences or behavioral triggers, resulting in a higher level of relevance and engagement.
Consumers today expect personalization. Generic advertisements often fall flat, while tailored experiences foster a sense of connection between the brand and the consumer. This connection can lead to increased loyalty and advocacy, essential components of long-term business success.
- Retargeting Strategies
Retargeting, or remarketing, is a powerful strategy within digital advertising that focuses on engaging users who have previously interacted with a brand but did not convert. By serving ads to these individuals as they browse other websites or social media platforms, businesses can remind them of their initial interest and encourage them to revisit the brand.
Effective retargeting requires thoughtful execution to avoid overwhelming potential customers with too many ads, which could lead to negative perceptions. Instead, strategically timed reminders combined with enticing offers can create a fine balance that nurtures leads down the sales funnel.
4. Types of Digital Advertising
Diverse forms of digital advertising cater to different objectives and audience preferences. Businesses should consider the following primary types when developing their advertising strategies.
4.1. Internet-Based Advertising
Internet-based advertising leverages the power of the web to deliver targeted messages to users. This category encompasses several formats, each with its unique benefits and considerations.
- Social Media Advertising
Social media advertising capitalizes on the immense popularity of platforms like Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and TikTok. Brands can utilize paid ad placements to reach users directly within their social feeds, allowing for natural integration with content consumption.
The ability to target social media ads based on users' demographics, interests, and online behaviors makes this form of advertising particularly effective. Furthermore, the variety of ad formats—ranging from sponsored posts to carousel ads—enables brands to experiment and discover what resonates best with their audience.
- Search Advertising
Search advertising revolves around promoting products or services on search engine results pages (SERPs). When users type relevant keywords into search engines like Google or Bing, search ads appear prominently, offering a direct response to user intent.
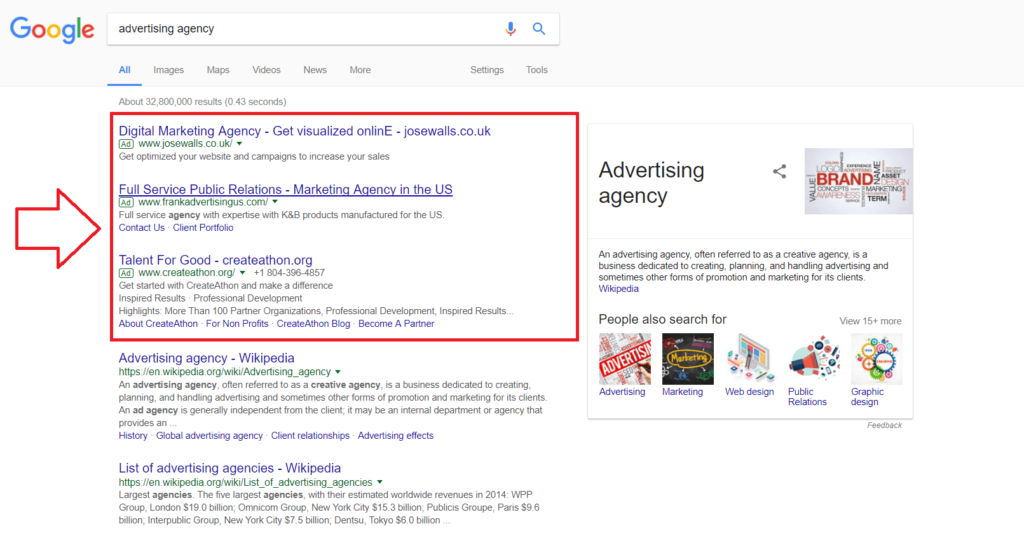
This approach is particularly advantageous for capturing high-intent customers actively seeking solutions. By bidding on keywords that align with their offerings, advertisers can position themselves at the forefront of potential buyers’ searches, ultimately leading to increased visibility and conversions.
- Display Advertising
Display advertising encompasses a wide range of visual ad formats that appear on websites, apps, and social media platforms. These ads can include static images, videos, banners, and rich media elements designed to attract attention.
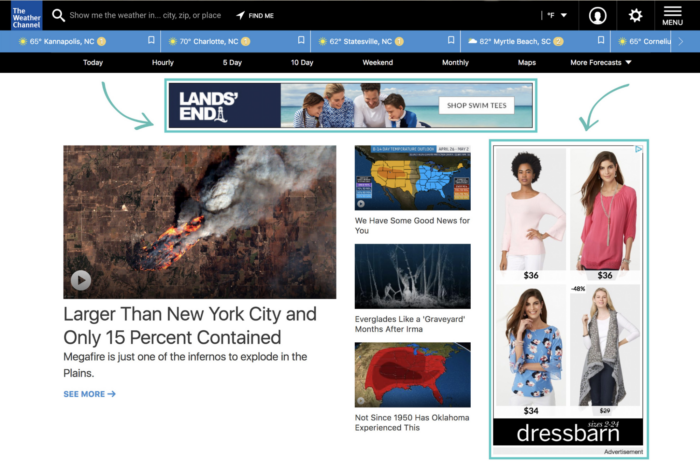
While display ads can help increase brand awareness and drive website traffic, achieving high engagement rates remains a challenge. To mitigate this, advertisers can utilize advanced targeting techniques to ensure their ads reach the right audiences across relevant platforms.
- Audio Advertising
Audio advertising has gained traction due to the proliferation of streaming services and podcasts. Advertisers can seamlessly integrate their messages into audio content, providing listeners with relevant promotions during their favorite shows or music playlists.
Whether it's a pre-roll ad before a podcast episode or an advertisement played during a song on a streaming platform, audio advertising captures audience attention in a non-intrusive manner. This format often lends itself to creating memorable narratives, fostering deeper connections with consumers.
- Online Video Advertising
Video advertising continues to dominate the digital landscape. Whether through pre-roll ads on video content platforms like YouTube or short-form clips on social media, video has proven to be an effective storytelling medium.
With the ability to convey complex messages in an engaging format, video ads can enhance brand recognition and drive action. Additionally, video allows for creative experimentation, enabling brands to leverage animation, testimonials, and immersive storytelling techniques to captivate their audience.
4.2. Device-Based Advertising
Device-based advertising utilizes various electronic devices to deliver messages to consumers, enabling brands to engage audiences in different contexts.
- Television Advertising
Television advertising remains a powerful force in the digital advertising landscape, particularly with the advent of smart TVs and streaming platforms. Brands can reach vast audiences during live broadcasts, news programs, or popular series.
Despite the competitive nature of TV ad slots, businesses can harness data-driven insights to optimize their targeting. Geographic and demographic segmentation can ensure that ads reach specific viewers, enhancing the overall effectiveness of television campaigns.
- Radio Advertising
Radio advertising offers an opportunity to engage audiences during commutes, workouts, or leisure activities. Advertisers can sponsor segments or run standalone ads on radio stations to enhance brand visibility.
While radio may not provide the same level of targeting as digital channels, it can still be a valuable tool for generating brand awareness and reaching specific demographics based on station popularity and listener preferences.
- Digital Out-of-Home (DOOH) Advertising
Digital out-of-home (DOOH) advertising refers to multimedia advertising displayed on digital screens in public spaces. These screens can be found in shopping malls, airports, transit stations, and urban centers, delivering messages to on-the-go consumers.

DOOH combines the immediacy of digital advertising with the broad reach of traditional outdoor advertising. With programmatic buying capabilities, advertisers can dynamically adjust their messaging based on real-time data, ensuring relevance and effectiveness.
5. Pricing Models in Digital Advertising
Understanding the pricing models used in digital advertising is crucial for businesses looking to allocate their budgets effectively and achieve optimal returns.
- Cost per Mille (CPM)
Cost per mille (CPM), or cost per thousand impressions (CPT), is a widely used model in digital advertising where advertisers pay a fixed amount for every 1,000 times their ad is displayed. This pricing structure is commonly employed for brand awareness campaigns, where the objective is to maximize reach rather than immediate conversions.
Advertisers can utilize CPM to assess the effectiveness of their campaigns in terms of visibility and exposure. It works best for campaigns focused on building awareness and familiarity rather than direct response.
- Cost per Click (CPC)
Cost per click (CPC) is a performance-based pricing model where advertisers only pay when a user clicks on their ad. This model incentivizes advertisers to create compelling ads that encourage engagement.
CPC is especially popular in search advertising, where advertisers bid on keywords to secure ad placements. This model ensures that businesses only incur costs when users express interest by clicking, making it a cost-efficient option for driving targeted traffic.
- Cost per Engagement (CPE)
Cost per engagement (CPE) measures the cost associated with each user interaction with an ad. Engagement can encompass various actions, such as likes, shares, comments, or watching a video ad for a specified duration.
CPE aligns well with social media advertising, where interactions play a pivotal role in gauging ad effectiveness. Tracking engagement allows advertisers to refine their strategies and focus on fostering meaningful connections with their audience.
- Cost per View (CPV)
Cost per view (CPV) is primarily associated with video advertising, where advertisers pay each time a user views their video ad. This model can be advantageous for brands seeking to promote their products through engaging video content.
By using CPV, advertisers can prioritize captivating storytelling and produce high-quality video ads that resonate with viewers. This approach emphasizes the importance of retaining viewer attention, as longer watch durations can signal higher engagement levels.
- Cost per Lead (CPL)
Cost per lead (CPL) centers around generating leads through advertisements. Advertisers pay a set fee for each qualified lead generated, making it a viable model for businesses aiming to gather contact information from potential customers.
CPL is particularly useful for B2B companies and industries with longer sales cycles, as it aligns the cost of advertising with the value of acquiring leads that can be nurtured into paying customers over time.
- Cost per Action (CPA)
Cost per action (CPA) is another performance-driven model where advertisers pay only when a specific action occurs, such as a sale, sign-up, or download. This model encourages advertisers to focus on outcomes rather than just clicks or impressions, aligning their goals with measurable results.
CPA can be beneficial for e-commerce businesses and those desiring clear accountability in their advertising spend, as it emphasizes return on investment.
- Cost per Install (CPI)
Cost per install (CPI) applies specifically to mobile app advertising, where businesses pay for each installation of their app driven by a digital ad. This model is essential for app developers seeking to grow their user base.
By focusing on CPI, advertisers can assess the effectiveness of their campaigns in attracting app downloads, facilitating growth in a competitive mobile market.
6. Key Metrics for Measuring Digital Advertising Performance
To gauge the success of digital advertising efforts, businesses must focus on key performance metrics that provide insights into campaign effectiveness.
- Understanding Marketing Funnels
Marketing funnels represent the journey potential customers take from discovering a brand to making a purchase. Understanding this funnel helps advertisers identify key touchpoints and tailor their strategies accordingly.
The funnel typically consists of stages such as awareness, consideration, conversion, and retention. By measuring performance at each stage, businesses can refine their approaches and address any bottlenecks hindering customer progress toward conversion.
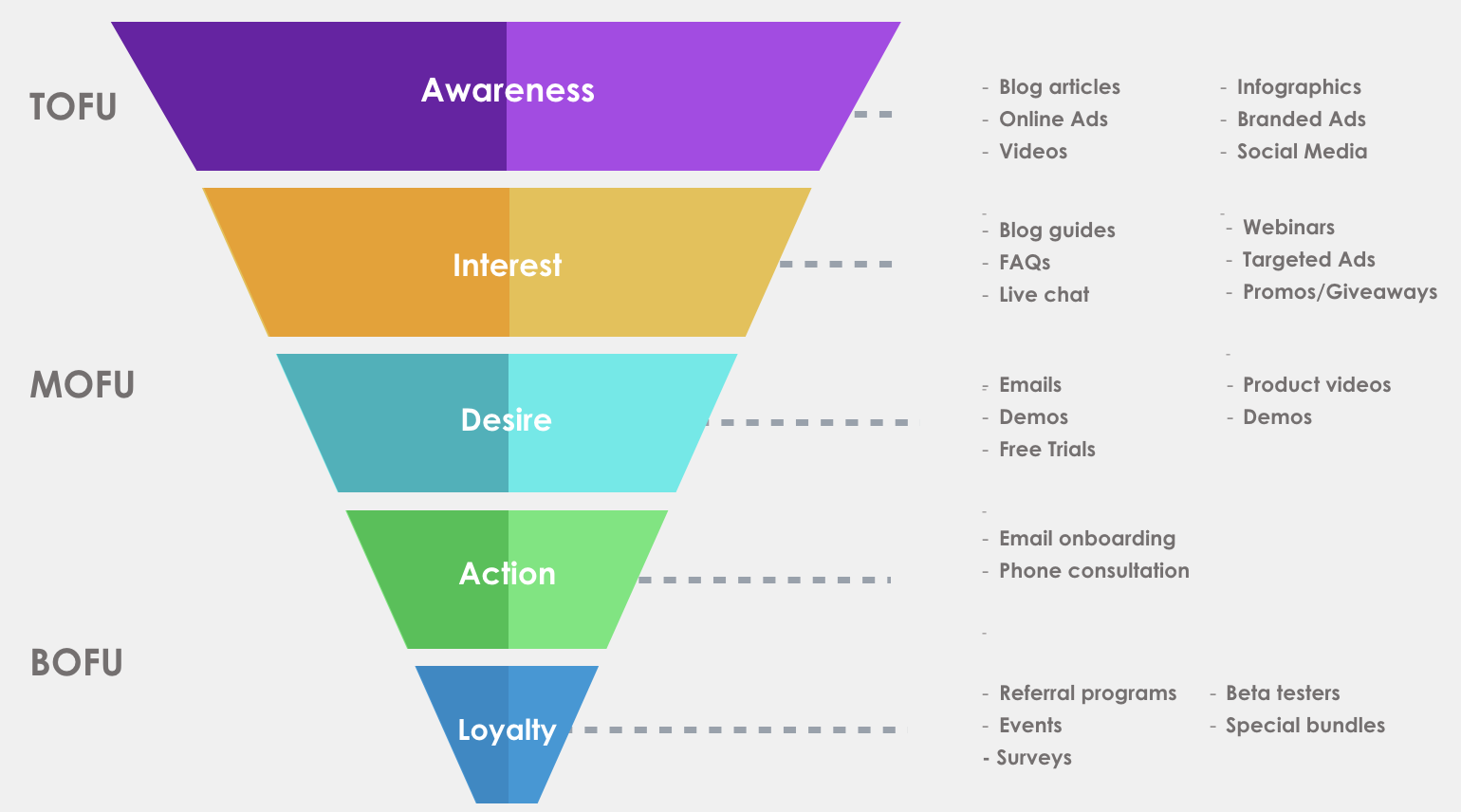
- Metrics for Brand Awareness
Brand awareness metrics focus on how well consumers recognize and recall a brand. Common indicators include reach, impressions, and frequency. Monitoring these metrics helps advertisers understand how effectively their campaigns are exposing their brand to potential customers.
Engagement metrics, such as shares and mentions, also contribute to assessing brand awareness. Higher levels of engagement indicate that consumers find the content valuable, reinforcing brand visibility and recognition.
- Metrics for Engagement
Engagement metrics measure how actively users interact with digital ads. Key indicators include click-through rates (CTR), time spent on landing pages, and social media interactions. High engagement levels suggest that the content resonates with the target audience, prompting action.
Analyzing engagement metrics allows advertisers to refine their messaging and optimize ad placements for maximum impact, ultimately enhancing overall campaign performance.
- Metrics for Conversion
Conversion metrics focus on the ultimate goal of advertising: turning prospects into paying customers. Key conversion metrics include conversion rates, sales numbers, and return on ad spend (ROAS). Understanding these metrics helps businesses assess the effectiveness of their campaigns in generating revenue.
Additionally, tracking the cost per acquisition (CPA) provides insights into the financial efficiency of digital advertising efforts, enabling businesses to make informed budget decisions.
7. Best Practices for Successful Digital Advertising Campaigns
Implementing best practices can significantly enhance the effectiveness of digital advertising strategies. Here are some key principles to consider.
- Identifying Your Target Audience
A deep understanding of your target audience is foundational for successful digital advertising. Identifying key demographics, interests, and behaviors helps shape ad messaging and placement strategies.
Utilizing market research, customer personas, and data analytics tools can provide valuable insights into your audience's preferences and pain points. This knowledge ensures that your ads resonate with potential customers, increasing the likelihood of engagement and conversion.
- Setting Clear Objectives
Defining clear, measurable objectives is essential for evaluating the success of digital advertising campaigns. Whether your goal is to boost brand awareness, drive website traffic, generate leads, or increase sales, establishing specific KPIs enables effective performance tracking.
Setting SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals aligns team efforts and ensures everyone is working toward a common purpose, ultimately guiding strategic decision-making throughout the campaign.
- Choosing the Right Platforms
Selecting the appropriate advertising platforms is vital to reaching your intended audience. Different platforms cater to distinct demographics and interests, so understanding where your target audience spends their time is crucial.
For instance, younger audiences may gravitate toward platforms like TikTok and Instagram, while B2B marketers might find better success on LinkedIn. Tailoring your ad placements to align with audience preferences maximizes the effectiveness of your campaigns.
- Crafting Compelling Ad Content
Content is king in the world of digital advertising. Compelling ad copy, engaging visuals, and strong calls-to-action are essential for capturing attention and driving action.
Investing in high-quality creatives that align with your brand identity fosters trust and enhances the overall user experience. Experimenting with different formats and messages can help identify what resonates best with your audience, leading to improved engagement and conversion rates.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid in Digital Advertising
Even experienced marketers can fall prey to mistakes in digital advertising. Recognizing and avoiding these pitfalls can significantly enhance campaign performance.
- Neglecting Data Analysis
Data analysis is paramount in digital advertising. Failing to regularly review performance metrics can result in missed opportunities for optimization. Continuous monitoring allows advertisers to make data-driven decisions and fine-tune their strategies based on real-time insights.
When campaigns underperform, advertisers should delve into the data to identify patterns and areas for improvement. Ignoring this critical aspect can lead to wasted resources and diminished results.
- Failing to Test Ads
Testing different ad formats, messaging strategies, and audience segments can uncover valuable insights. A/B testing allows marketers to compare variations of their ads, helping identify the most effective elements.
Without proper testing, businesses may miss opportunities to enhance engagement and conversion rates. Regularly experimenting with new approaches fosters innovation and keeps campaigns fresh.
- Ignoring Mobile Optimization
With the increasing prevalence of mobile usage, optimizing digital ads for mobile devices is essential. Failing to do so can hinder the effectiveness of campaigns, resulting in poor user experiences and high bounce rates.
Businesses should ensure that their ads are responsive and visually appealing on smaller screens. Streamlined landing pages that load quickly and are easy to navigate enhance the chances of converting mobile users into customers.
- Overlooking Audience Segmentation
Audience segmentation is vital for maximizing the impact of digital advertising. Treating all consumers as a single monolithic group can dilute the effectiveness of messaging and positioning.
Segmentation allows businesses to tailor their campaigns to various audience subgroups based on interests, demographics, and behaviors. This personalized approach results in more relevant and engaging ads, ultimately driving better performance.
9. Notes on Digital Advertising Trends
Staying abreast of emerging trends in digital advertising is crucial for businesses aiming to remain competitive. Here are some key developments shaping the industry.
- The Rise of Influencer Marketing
Influencer marketing has surged in popularity as brands seek authentic connections with consumers. Partnering with influencers allows brands to tap into established communities and gain credibility among followers.
Effectively leveraging influencer relationships can enhance brand visibility and foster trust, resulting in increased engagement and conversions. Adopting a strategic approach to influencer partnerships ensures that brands align with individuals whose values resonate with their target audience.
- Increased Focus on Video Content
The demand for video content continues to rise across digital platforms. Consumers prefer video due to its engaging nature and ability to convey complex messages in a concise format.
Brands should prioritize video advertising in their strategies, utilizing different formats such as live streams, tutorials, and storytelling to connect with their audiences. Staying ahead of video trends positions brands favorably in a crowded marketplace.
- Growing Importance of Privacy Regulations
As privacy regulations and consumer concerns regarding data security intensify, digital advertisers must adapt their strategies accordingly. Compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA is imperative for navigating the evolving landscape.
Fostering transparency in data collection and usage builds consumer trust, reinforcing positive brand perceptions. Focusing on ethical data practices ensures long-term sustainability for digital advertising initiatives.
10. Conclusion
In conclusion, digital advertising plays an integral role in modern marketing strategies, offering businesses unprecedented opportunities to engage and convert consumers. By understanding its characteristics, types, pricing models, performance metrics, and best practices, marketers can develop effective campaigns that drive results.
As digital landscapes continue to evolve, businesses must remain agile and adaptable, incorporating emerging trends while staying true to their brand values. Implementing the knowledge gained from this guide can empower organizations to navigate the complexities of digital advertising and harness its full potential for sustainable growth.
Digital advertising is a way for affiliate marketers to increase traffic and conversions. Affiliate marketing is becoming more and more popular and has more participants. These two articles will provide you with the information you need when starting to participate in affiliate marketing.
- How to make money with affiliate marketing for beginners by using Hidemyacc?
- Must-have best affiliate marketing tools to boost your sales & conversions
- Affiliate Marketing Arbitrage - Tips to Increase Traffic
11. FAQ
What is the difference between digital advertising and online advertising?
Digital advertising encompasses a broad range of advertising methods delivered through electronic devices, including both internet-based and device-based formats. Online advertising is a subset of digital advertising, specifically referring to ads served over the internet.
How can I measure the success of my digital ads?
Success can be measured through various performance metrics, including engagement rates, conversion rates, return on ad spend (ROAS), and more. Establishing clear objectives and monitoring relevant metrics allows businesses to assess the effectiveness of their campaigns.
What budget should I allocate for digital advertising?
Budget allocation depends on factors such as campaign goals, target audience, and selected platforms. It's essential to start with a clear understanding of objectives and test different approaches to determine the most effective allocation of resources.






