WebRTC is a core technology behind real-time communication on the modern web, enabling browsers to exchange audio, video, and data without relying on plugins or external software. From video calls and live chats to interactive web applications, WebRTC plays a critical role in how users and businesses communicate online today.
In this article, Hidemyacc will explain what WebRTC is, how it works at a high level, and why it has become an essential part of modern browser-based communication. You’ll also learn the key benefits of WebRTC and how it can be managed effectively in different browsing environments.
1. Introduction - WebRTC and Modern web communication
WebRTC has quietly become one of the foundational technologies behind real-time communication on the modern web. Many of the interactions users rely on every day, such as browser-based video calls, live chat features, and highly interactive web applications, are powered by WebRTC running in the background.
From virtual meetings and customer support chats to collaborative tools and online platforms, WebRTC enables browsers to communicate instantly without requiring additional plugins or external software. This seamless experience is why most users interact with WebRTC daily without ever noticing it.
As web applications continue to evolve beyond static pages into fully interactive platforms, real-time communication is no longer optional, it is expected. WebRTC makes this possible by allowing browsers to send and receive audio, video, and data efficiently, directly, and with minimal latency.
More importantly, WebRTC is not just about improving user experience. It also plays a role in how browsers establish connections, manage communication channels, and behave within modern web environments. Understanding WebRTC helps clarify how today’s browsers communicate and why this technology has become a core component of the modern internet.

>>> Internet infrastructure: What it is and why it matters
2. What is WebRTC?
2.1 Definition of WebRTC
WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication) is an open web standard that enables real-time audio, video, and data communication directly between browsers and devices. It is built into modern browsers and does not require plugins, extensions, or additional software.
Developed and standardized by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), WebRTC provides a set of APIs that allow browsers to communicate with each other in real time using secure, peer-to-peer connections.
In simple terms, WebRTC allows voice, video, and data communication to work natively inside web pages and applications, making real-time interaction a core capability of the modern web.
With broad support across major browsers and operating systems, WebRTC has become a foundational technology for browser-based communication and interactive web experiences.
2.2 Where is WebRTC used?
WebRTC is widely adopted across many real-world applications, including:
- Video conferencing applications (browser-based meetings and calls)
- Customer support live chat systems with audio or video features
- Online collaboration tools for teams and remote work
- Real-time web applications that require instant data exchange
Because WebRTC enables direct, low-latency communication between users, it is especially well suited for applications that rely on real-time interaction rather than delayed, server-based messaging.
Source:
3. How does WebRTC work?
WebRTC enables real-time communication by establishing a direct connection between devices and allowing them to exchange audio, video, and data efficiently. All of this happens at the browser level, without requiring plugins or external software, making the process seamless for both users and developers.
At a simplified level, a WebRTC connection follows this flow:
User’s device → STUN/TURN services → Peer-to-peer communication channel → Recipient’s device
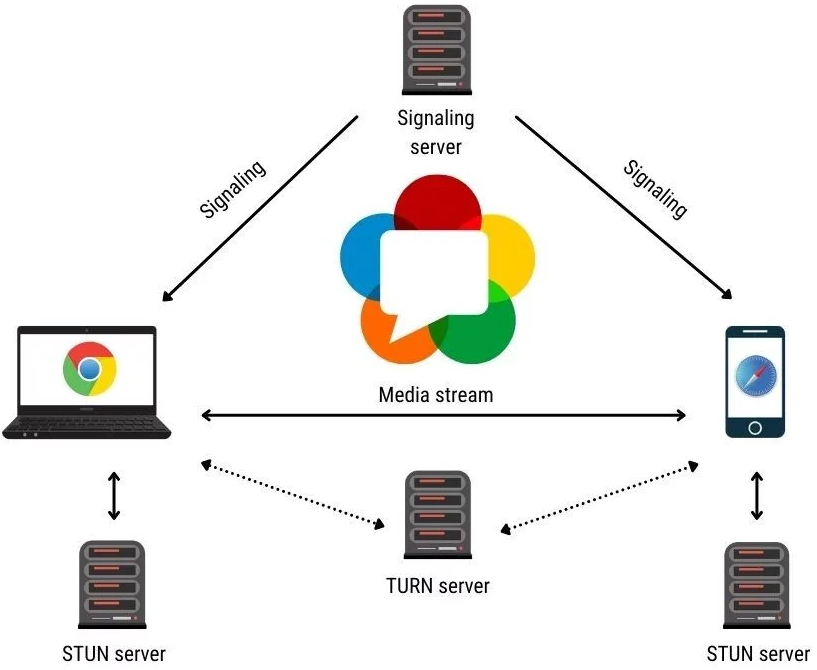
3.1 Establishing a peer-to-peer connection
When a WebRTC-based audio or video call begins, the application first needs to connect all participating devices. Instead of sending media through a central server, WebRTC is designed to create a peer-to-peer (P2P) communication channel whenever possible.
Modern networks often involve firewalls and different network configurations. To handle this complexity, WebRTC automatically determines how devices can reach each other and selects the most efficient connection method available. This process is handled transparently in the background, without user interaction.
By using a peer-to-peer approach, WebRTC minimizes latency and delivers a smoother real-time communication experience.
3.2 Connection setup and real-time data exchange
Once the connection parameters are established, WebRTC opens a private communication channel between the participating devices. Through this channel, browsers can:
- Transmit audio and video streams in real time
- Exchange data for messaging, file transfer, or synchronization
- Maintain responsive, low-latency communication
WebRTC relies on built-in browser APIs to access hardware such as microphones and cameras, capture media streams, and deliver them securely to the connected peers. Because only the devices involved in the session are aware of the connection details, communication remains isolated within the call.
3.3 The role of STUN and TURN (High-level overview)
To support connection establishment across different network environments, WebRTC uses auxiliary services such as STUN and TURN servers.
- STUN servers assist browsers in determining how they can communicate with other devices.
- TURN servers provide a relay mechanism when a direct peer-to-peer connection is not feasible.
These services help WebRTC navigate complex network conditions and ensure that real-time communication can be established reliably, without exposing users or developers to low-level networking details.
4. Why WebRTC is important for modern websites
WebRTC is more than a technical feature, it has become a core building block of modern web experiences. As users expect faster, more interactive, and more natural communication online, WebRTC enables websites to meet those expectations directly in the browser.
4.1 Improving user experience with Real-time interaction
Modern users value speed, simplicity, and immediacy. WebRTC allows websites to deliver real-time communication without disrupting the user journey.
With WebRTC, websites can offer:
- Real-time audio and video communication inside the browser
- Low-latency interactions that feel natural and responsive
- A smooth experience with no additional software or plugin installation
By removing technical barriers, WebRTC helps websites keep users engaged and reduces friction during critical interactions such as support, collaboration, or live communication.
4.2 Strategic advantages for businesses and developers
From a business and development standpoint, WebRTC offers clear long-term advantages.
For businesses, WebRTC helps:
- Lower infrastructure and operational costs compared to traditional communication systems
- Launch real-time features faster without relying on external plugins or closed platforms
- Reach users across devices and operating systems through the browser
For developers, WebRTC provides:
- A standardized, browser-native solution supported by major platforms
- Faster development cycles thanks to built-in APIs
- A scalable foundation for adding real-time features as products grow
This combination makes WebRTC an attractive choice for both startups and enterprise-level web projects.
4.3 WebRTC and the rise of interactive web applications
The web is evolving beyond static pages. Modern web applications increasingly replace traditional desktop software by offering richer, more interactive experiences.
WebRTC plays a key role in this shift by enabling:
- Browser-based applications that support live communication and collaboration
- Real-time features that were previously limited to native desktop apps
- A more unified web ecosystem where communication happens instantly
As web applications continue to grow in capability and complexity, WebRTC remains a foundational technology powering the next generation of interactive websites.

5. Benefits of WebRTC
WebRTC was created to help developers deliver high-quality real-time communication directly in the browser, without unnecessary complexity. Below are the key benefits that make WebRTC a widely adopted standard for modern web applications.
5.1 Performance
WebRTC is optimized for real-time performance, making it suitable for audio, video, and data communication.
Key performance advantages include:
- Low latency, enabling natural, real-time conversations
- Direct peer-to-peer data transmission, reducing unnecessary intermediaries
- Modern audio and video codecs that maintain quality even on unstable or slow connections
These characteristics allow WebRTC to deliver clear audio, smooth video, and responsive data exchange.
5.2 Compatibility
One of WebRTC’s strongest advantages is its broad compatibility across platforms and devices.
WebRTC:
- Is supported by most modern browsers
- Works across desktop and mobile operating systems
- Integrates smoothly with HTML5 and modern web technologies
Thanks to its open-source foundation, WebRTC continues to evolve alongside browsers, ensuring long-term compatibility for web applications.
5.3 Security at the protocol level
WebRTC includes mandatory encryption at the protocol level to protect real-time communication.
By default, WebRTC:
- Encrypts audio, video, and data streams
- Helps ensure secure transmission between connected peers
It is important to note that security does not equal anonymity WebRTC focuses on protecting communication content, not hiding user identity or network information.
6. WebRTC as part of browser behavior and fingerprinting
WebRTC is not only a communication technology, it is also part of how modern browsers handle connections and interact with the network environment.
From a technical standpoint, WebRTC reflects:
- How a browser establishes real-time connections
- How it interacts with underlying network conditions
- How certain browser capabilities are exposed during communication setup
Because of this, WebRTC is often considered a technical component of the browser environment, alongside other browser behaviors that influence how web applications function and interact.
For specific professional groups such as developers, digital marketers, and technical operators, understanding and managing browser behavior is an important part of building, testing, and scaling web-based systems. In these contexts, WebRTC is viewed as one of several browser-level technologies that may require awareness and control, depending on the use case.
At this level, WebRTC should be understood as a functional browser mechanism, not inherently good or bad, but relevant within the broader context of modern web architecture and browser behavior management.
7. How to manage WebRTC with Hidemyacc
WebRTC is enabled by default in most modern browsers and plays an important role in real-time communication. For everyday users, this default behavior is usually sufficient. However, in more advanced use cases, managing how WebRTC behaves at the browser level can become necessary.
7.1 Why manage WebRTC instead of using default browser settings?
Modern browsers are designed to provide a one-size-fits-all experience. While this works well for general users, it offers limited flexibility for professional or large-scale workflows.
In practice:
- Each browser profile may require different behavior and configurations
- Default browser settings do not allow granular control over how WebRTC interacts with the browser environment
- Managing multiple profiles using the same default behavior can create inconsistencies during testing or operations
For these reasons, WebRTC management is often considered part of browser environment control, rather than a standalone feature.
7.2 How Hidemyacc helps change WebRTC
Hidemyacc approaches WebRTC management at the browser profile level, rather than modifying the browser globally.
With Hidemyacc:
- WebRTC is handled individually within each browser profile
- WebRTC behavior is aligned with other profile components, including:
- Proxy configuration
- Browser fingerprint settings
- The browser’s natural behavior is preserved, ensuring compatibility with real-world web applications
- This profile-based approach allows users to manage WebRTC consistently without breaking core browser functionality.
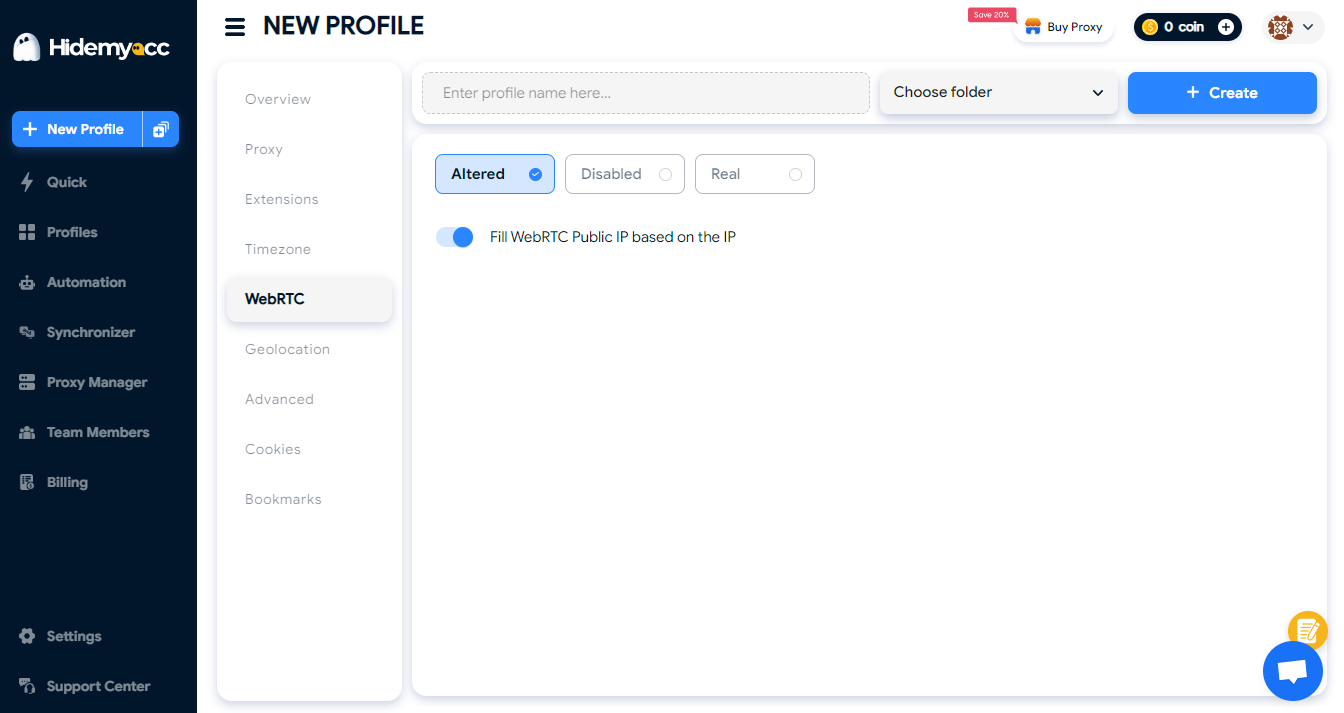
7.3 When should WebRTC be adjusted?
Adjusting WebRTC behavior is typically relevant in scenarios such as:
- Managing multiple browser profiles simultaneously
- Running testing or automation environments
- Operating structured multi-account workflows that require isolated browser environments
In these cases, WebRTC management becomes part of a broader strategy for maintaining consistency and control across browser profiles.
You should also have a basic understanding of Web Scraping when making money online. We have published a post about it recently. You can read it here.
8. Best practices when working with WebRTC
WebRTC is a core browser technology designed to support real-time communication. When working with WebRTC in professional environments, a balanced and informed approach helps maintain stability, compatibility, and long-term reliability.
8.1. Avoid over-modifying WebRTC behavior
WebRTC is deeply integrated into modern browsers. Making extreme or unnecessary changes can lead to unexpected behavior, compatibility issues, or broken real-time features.
Best practice is to:
- Adjust WebRTC only when there is a clear technical reason
- Avoid disabling or heavily altering it without understanding the broader impact on browser behavior
8.2. Be cautious with third-party extensions
Not all browser extensions handle WebRTC in a reliable or transparent way.
When using extensions:
- Avoid tools from unclear or unverified sources
- Be aware that extensions may interfere with native browser behavior
- Consider long-term stability and maintainability rather than quick fixes
Uncontrolled extensions can introduce inconsistencies that are difficult to diagnose later.
8.3. Keep WebRTC consistent with the browser environment
WebRTC works best when it aligns naturally with the overall browser setup.
This means:
- Keeping WebRTC behavior consistent with the browser profile
- Ensuring it matches related elements such as network configuration and browser capabilities
- Avoiding isolated changes that conflict with the rest of the environment
Consistency helps reduce unexpected results across sessions and profiles.
8.4. Prefer integrated solutions over fragmented adjustments
Managing WebRTC in isolation often creates more complexity.
Whenever possible:
- Use integrated, profile-based solutions
- Manage WebRTC as part of a broader browser environment strategy
- Avoid stacking multiple tools that modify similar browser components independently
An integrated approach leads to cleaner workflows and more predictable outcomes.
9. Conclusion
WebRTC has become a foundational technology of the modern web, enabling real-time communication directly inside the browser. From video calls to interactive web applications, it plays a key role in how today’s websites connect users in real time.
A clear understanding of WebRTC helps:
- Developers build more reliable and interactive web applications
- Marketers and operators better manage browser environments across different workflows
As WebRTC is closely tied to overall browser behavior, managing it at the profile level can provide greater consistency and control in professional use cases.
Hidemyacc allows users to manage WebRTC within individual browser profiles, making it easier to align WebRTC behavior with the broader browser environment without disrupting natural browser functionality.
Another article:
- What is a user agent? Examples, history, and how to change it
- How to check and enable WebGL fingerprint?
- Insight about Canvas Fingerprint
10. FAQ
What is WebRTC?
WebRTC is a browser-based technology that enables real-time audio, video, and data communication without plugins.
What is WebRTC used for?
WebRTC is used for video calls, voice communication, real-time messaging, and interactive web applications.
Does WebRTC require plugins?
No, WebRTC works natively in modern browsers and does not require any plugins or additional software.
Which browsers support WebRTC?
WebRTC is supported by major modern browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Safari.
Can WebRTC be managed or configured?
Yes, WebRTC behavior can be managed at the browser or profile level in advanced or professional use cases.






