If you have ever thought about starting an online business, you have probably heard about Amazon FBA. FBA, which stands for “Fulfillment by Amazon,” has helped thousands of entrepreneurs grow their stores by relying on Amazon’s massive logistics network. From storage and packaging to shipping and customer service, Amazon takes care of the hardest parts of selling online, leaving sellers with more time to focus on products and marketing.
This guide will explain in detail what Amazon FBA is, how it works, what it costs, the benefits and challenges, and whether it is the right option for your business. By the end, you will not only know what is Amazon FBA but also how to decide if it can truly help you succeed.
1. What is Amazon FBA? Definition and key components
So, what is Amazon FBA exactly? Amazon FBA, or Fulfillment by Amazon, is a service where sellers send their products to Amazon’s warehouses, known as fulfillment centers. Amazon then stores these products, picks and packs them when a customer places an order, ships the order to the buyer, and even handles returns and customer service.
This system allows sellers to benefit from the speed and reliability of Amazon Prime shipping. Shoppers trust the Amazon brand, and the FBA badge often increases sales because customers know their orders will arrive quickly and reliably.
To fully understand what is Amazon FBA, it helps to break down its main components. These include inventory storage, order picking and packing, fast shipping, professional customer service, and in many cases, multi-channel fulfillment for sales outside of Amazon. Together, these services form the backbone of the FBA program.
2. How does Amazon FBA work? A step-by-step explanations
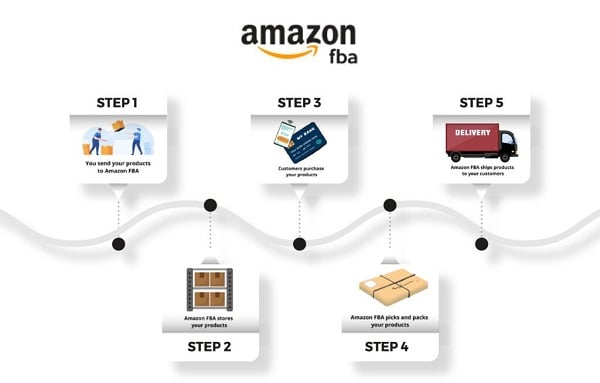
When people ask what Amazon FBA is, the answer is more than just “Amazon ships your products.” It’s a process that covers every stage of order fulfillment.
First, a seller creates an Amazon seller account and selects FBA as the fulfillment option. Then the seller prepares products according to Amazon’s packaging and labeling rules. Every item must be properly packed and barcoded so Amazon can track it in its system.
Next, the seller creates a shipping plan in Seller Central, sends products to Amazon’s fulfillment centers, and waits for Amazon to receive and scan them. Once the products are checked in, they become available for sale.

When a customer places an order, Amazon employees pick, pack, and ship it using their logistics network. Since most FBA items qualify for Prime, customers usually get two-day or even same-day delivery. If the customer returns the product, Amazon manages the refund and restocking.
This step-by-step process is why so many sellers find FBA convenient. It takes over the logistics side of e-commerce, allowing sellers to focus on sourcing and marketing.
3. Costs and fees of Amazon FBA
Understanding what is Amazon FBA also means understanding the costs. Using Amazon’s fulfillment system is powerful, but it comes at a price.
The first cost is the referral fee. This is a percentage of each sale, usually between 8% and 15% depending on the category. Fulfillment fees are next, and these cover the picking, packing, and shipping of each item. The exact fee depends on product size and weight.
Storage fees are another factor. Sellers pay monthly for warehouse space, and if products sit unsold for too long, long-term storage fees apply. Other expenses may include labeling, removal of unsold items, disposal, and return processing.
For example, selling a $30 item might involve a $4.50 referral fee, a $4 fulfillment fee, and a few cents of storage, leaving only part of the price as profit. This is why sellers researching what is Amazon FBA must calculate carefully before committing.
4. Pros and cons of Amazon FBA
A balanced look at what is Amazon FBA should include both benefits and drawbacks.
4.1. Advantages of Amazon FBA
The most obvious benefit is Prime shipping. Products fulfilled by Amazon often sell faster because customers trust the Prime badge. Sellers also save time since Amazon manages storage, packing, shipping, and returns. This allows businesses to scale more easily.
Another advantage is improved customer experience. Buyers get reliable delivery and professional service, which often leads to positive reviews. For those aiming to sell internationally, Amazon’s fulfillment network provides access to multiple marketplaces worldwide.
4.2. Disadvantages of Amazon FBA
On the other side, fees can eat into profits. Large or low-margin products may not be suitable for FBA. Sellers also lose some control over packaging and branding, since Amazon uses its own standard materials.
Inventory restrictions can cause problems too. During busy seasons, Amazon may limit how much stock sellers can send. Easy returns may also increase return rates. And, of course, sellers must follow Amazon’s rules, which can change at any time.
5. Is Amazon FBA right for your business?
A common follow-up question after asking what is Amazon FBA is whether it’s the right model for you. The answer depends on your products and goals.
FBA is excellent for small, lightweight, and high-demand products with healthy profit margins. It is also perfect for sellers who want to scale quickly without building a logistics system.
But if you sell bulky items or products with thin margins, FBA might reduce profitability too much. Businesses that value full control over packaging or branding may also prefer alternatives. The key is to run the numbers and test small shipments before going all in.
6. Alternatives and hybrid models
When people ask what is Amazon FBA, they often want to compare it with other models. One alternative is Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM), where sellers store and ship products themselves. Another is Seller-Fulfilled Prime, which allows sellers to keep logistics in-house while still offering Prime shipping, though it requires strict standards.
Third-party logistics providers, also known as 3PLs, can handle warehousing and shipping outside of Amazon. Dropshipping is another model, where products are sent directly from suppliers to customers. Many sellers use hybrid approaches, combining FBA for certain items with FBM or 3PLs for others.
7. International and regional considerations
Anyone asking what is Amazon FBA should also consider global aspects. The program operates in many regions, including North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. However, rules and fees differ by location.
For example, European sellers must account for VAT, customs, and product compliance. Shipping inventory across borders also requires handling duties and paperwork. A product that works well in the U.S. might not be profitable elsewhere once taxes and logistics are factored in.
8. Best practices for success with Amazon FBA
To make the most of FBA, sellers need to apply best practices. Inventory management is critical to avoid stockouts or long-term storage fees. Proper product preparation reduces damage and penalties.
Using Amazon’s FBA calculator helps sellers estimate profits accurately. Choosing the right products—usually small, lightweight, and high-demand items—can make the difference between success and failure. Pricing strategies and customer reviews also play a major role.
Finally, sellers should forecast demand ahead of peak seasons to ensure stock is available. By applying these practices, sellers who wonder what is Amazon FBA can move from theory to profitable results.
9. Case studies and examples
One seller who specialized in kitchen tools used FBA to reach Prime customers. Sales grew rapidly because the products were lightweight, affordable, and easy to ship. Within a year, the business expanded significantly.
In contrast, a furniture seller struggled with FBA. Storage and shipping fees for large items made profits unsustainable. They eventually switched to a hybrid model, keeping smaller items in FBA and fulfilling larger orders themselves.
These examples highlight that knowing what is Amazon FBA is only the beginning—success depends on product choice and careful planning.
10. Conclusion
So, what is Amazon FBA? It is Amazon’s fulfillment program that takes care of storage, shipping, and customer service for sellers. It makes scaling easier, improves customer trust, and gives access to Prime shoppers.
But FBA is not free of challenges. Costs, restrictions, and less control can make it unsuitable for certain businesses. Sellers must analyze their products, margins, and goals before deciding.
For many, though, FBA is a game-changer. By knowing exactly what is Amazon FBA and how it works, you can make smarter choices and potentially grow your business faster.
>>> More about Amazon:
- Merch by Amazon: How to Make Money Selling Custom Products
- Open multiple Amazon seller accounts: Legal and grayhack method
- Top 17 Amazon SEO tools that help you rank: Boost your sales now!
- 13 Amazon seller tools you wish you knew earlier
11. FAQ
Can anyone use Amazon FBA?
Yes, as long as you have a seller account, though some products face restrictions.
What happens if products don’t sell?
Amazon can return or dispose of unsold inventory, but fees apply.
How long does it take to process inventory?
Usually a few days, but longer during busy periods.
How do I estimate costs?
Use Amazon’s FBA calculator to see fees before committing.






