DNS plays an important role in converting domain names into IP addresses to access websites on the Internet. Clearly understand What is DNS?, the way this tool works and functions will help you optimize your web surfing experience as well as improve access speed. This article will provide detailed instructions on DNS and how to use DNS most effectively to improve security and network connection performance.
1. What is DNS?
DNS, short for Domain Name System, is a domain name management and resolution system that helps determine the IP addresses corresponding to websites or resources on the Internet. When you enter a URL into your browser, DNS is used to find out the IP address of the server containing that website, helping the browser connect correctly.
In addition to resolving domain names for websites, DNS also supports other services such as email addresses, FTP servers and many other network services. Furthermore, DNS also provides security features such as digital signatures and encryption, to protect information when transmitted over the network.
2. What is DNS used for?
Outside What is DNS?, many people also wonder what DNS is used for? It can be said, DNS Server plays an important role in converting domain names into IP addresses, allowing browsers to access and connect to websites or resources on the internet. Specifically, DNS Server has the following functions:
- Domain name resolution: DNS Server converts the domain name of a website into the IP address of the server containing that website. When a user enters a domain name into the browser, the system will send a request to DNS Server to find the corresponding IP address.
- Storing DNS information: DNS Server stores data related to domain names and IP addresses. When there is a search request, the system will query from its database to determine the IP address associated with that domain name.
- Update DNS information: DNS Server can be set up to automatically or manually update information about domain names and IP addresses. Network administrators or DNS management tools will do this.
- Increase access speed: DNS Server improves access speed by storing DNS information in cache. This helps shorten query response time by retrieving data from cache instead of querying to another server.
- DNS information security: DNS Server can be configured to protect the security of DNS data through measures such as encryption, digital signatures, and user authentication. These features help ensure that DNS information is transmitted securely, preventing it from being stolen.
3. How DNS Works
When you type a website address like hidemyacc.com in your browser, your computer doesn’t actually understand names - it only understands IP addresses (like 104.26.9.233).
DNS (Domain Name System) works like the Internet’s phone book, translating domain names into IP addresses so your browser knows where to go.3.1. Your device asks the DNS Resolver
Your computer or browser first sends a question to a DNS resolver (usually from your internet provider or a public one like Google DNS 8.8.8.8 or Cloudflare 1.1.1.1):
“What is the IP address of hidemyacc.com?”
If the resolver already knows the answer (saved in cache), it replies right away. If not, it starts looking for it.
3.2. The Resolver asks the Root Server
The root server is the top level of the DNS system. It doesn’t know the exact IP, but it knows which server handles .com, .org, .net, etc. So it says: “Ask the .com server.”
3.3. The Resolver asks the TLD Server (.com, .org, .vn, …)
The TLD (Top-Level Domain) server for .com knows which DNS server is responsible for hidemyacc.com. It replies: “You can find hidemyacc.com at this specific DNS server.”
3.4. The Resolver asks the Authoritative DNS Server
Finally, the resolver contacts the authoritative DNS server - the “official” one for that domain. This server contains the actual DNS records and gives the final answer: hidemyacc.com → 104.26.9.233
The resolver saves this result (for faster use next time) and sends it back to your browser.
3.5. Browser connects to the website
Now your browser uses that IP to connect to the real web server and loads the website for you.
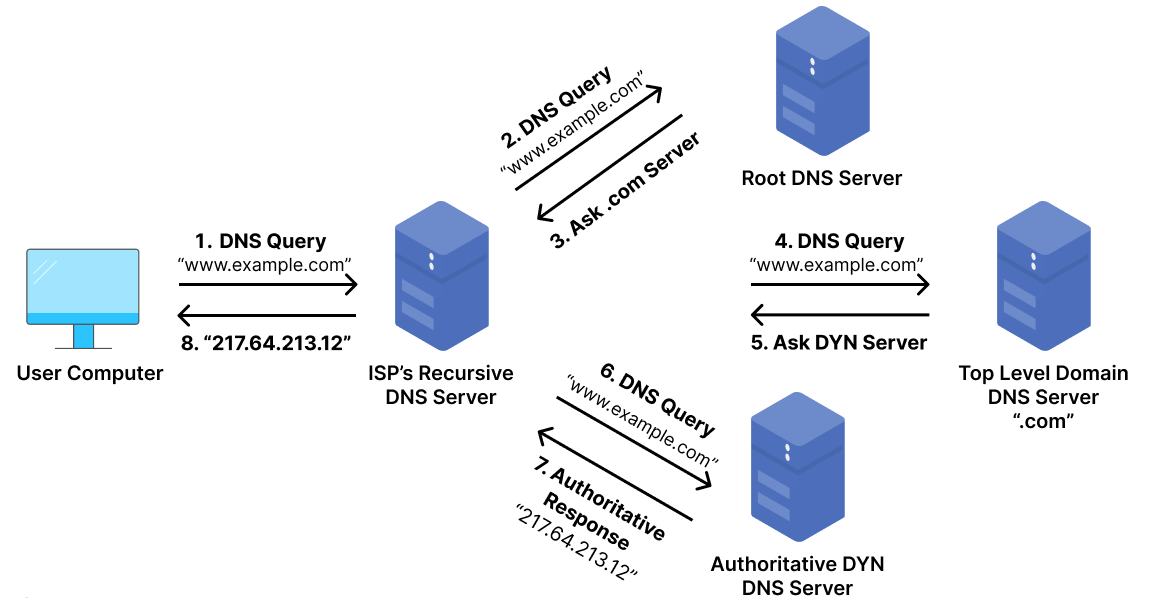
Summary: Browser → DNS Resolver → Root Server → TLD Server → Authoritative Server → Returns IP → Website loads
Extra Tip for Readers
Today, the whole DNS process happens very fast, usually in just a few milliseconds thanks to DNS caching. Caching means your computer and DNS servers remember the results for a short time, so the next time you visit the same website, it loads almost instantly.
Modern DNS providers like Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) and Google DNS (8.8.8.8) also support DNS over HTTPS (DoH) and DNS over TLS (DoT). These technologies encrypt your DNS requests, making it harder for anyone like your internet provider or hackers to see which websites you’re visiting.
Using encrypted DNS helps improve privacy and security every time you go online.
4. Types of DNS Servers explained
DNS can be categorized in different ways depending on how it works, where it’s used, and how secure it is. Understanding these categories helps you see what happens behind the scenes every time you visit a website
4.1. Based on the Role in the Query Process
When you type a domain like google.com, your device doesn’t connect directly to that website. Instead, it sends a request to a recursive DNS server (also called a resolver). This server, usually provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or a public service like Google DNS or Cloudflare DNS, acts like a helper - it looks for the correct IP address on your behalf.
If the resolver doesn’t already know the answer, it follows a path:
- It first checks the Root DNS Server, which tells it where to find the Top-Level Domain (TLD) server, for example,
.comor.org. - The resolver then contacts the TLD DNS Server, which points it to the Authoritative DNS Server - the one that stores the real record of the domain.
Once the authoritative server replies, your browser receives the correct IP address and loads the website.
In short: the recursive DNS asks, and the authoritative DNS answers that’s how your device finds its way online.
According to Cloudflare Learning Center, this process happens within milliseconds and involves multiple DNS servers working together in a chain of queries.
4.2. Based on usage scope
DNS servers can also be grouped by where and how they’re used.
- Public DNS:
Open to everyone on the Internet, easy to configure, and often faster than your default ISP’s DNS.
Popular examples include Google DNS (8.8.8.8), Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1), and Quad9 DNS (9.9.9.9).
These are great options if you want more speed, reliability, or privacy.
- Private (or Local) DNS:
Used inside companies or home networks to manage internal domain names - such as server.local or intranet.company.
This type helps improve internal speed and control which devices can access specific resources.
As explained by Google Developers, public resolvers like Google DNS aim to improve both performance and security compared to default ISP DNS.
4.3. Based on security level
Traditional DNS uses plain text communication (UDP port 53). That means your DNS requests and the websites you visit can be seen by anyone monitoring the network, including ISPs or attackers.
To improve privacy, modern DNS services now support encrypted protocols such as:
- DNS over HTTPS (DoH) - sends DNS requests through HTTPS, encrypting your activity like a secure web connection.
- DNS over TLS (DoT) - similar to DoH, but uses the TLS protocol for encryption, often used by routers or mobile systems.
These encrypted options make it much harder for third parties to track your browsing history.
According to Mozilla Developer Network, DNS over HTTPS helps protect users by encrypting requests and preventing potential eavesdropping or tampering.
5. Comparing popular public DNS resolvers
When you change your default DNS, public resolvers are usually the first choice. They’re fast, reliable, and free — but each service has its own advantages. The table below shows a quick comparison of the most popular ones:
| DNS Provider | Address | Main Focus | Privacy Policy | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Google DNS | 8.8.8.8 / 8.8.4.4 | Speed and global reliability | Keeps temporary logs for performance and abuse prevention (Google Developers) | Users who want stability and fast performance |
| Cloudflare DNS | 1.1.1.1 / 1.0.0.1 | Privacy and encryption | No IP logging, data deleted within 24 hours (Cloudflare) | Users who value privacy and security |
| Quad9 DNS | 9.9.9.9 | Security and threat blocking | Non-profit, no user tracking, blocks malicious domains (Quad9) | Users who want protection against malware and phishing |
| OpenDNS | 208.67.222.222 / 208.67.220.220 | Parental control and filtering | May retain anonymized logs for analytics (Cisco OpenDNS) | Families or small businesses needing content filtering |
In short, Google DNS is ideal if you prioritize performance, Cloudflare DNS suits privacy-conscious users, Quad9 focuses on security, and OpenDNS is great for managing safe browsing environments. You can even mix them depending on your goal, for example, using Cloudflare on your personal device while keeping OpenDNS for a home network.
>>> About public DNS
- Why Use 8.8.8.8 DNS? Improve Your Browsing with Google’s Public DNS
- 1.1.1.1 DNS: What Is It and How Can It Improve Your Internet Speed and Privacy?
- Google Public DNS Server: What It Is and How to Configure It for Faster Internet
6. DNS and privacy: what happens behind the scenes
Every DNS query reveals a small piece of your digital footprint. Each time you type a website address, your request passes through a DNS provider whether it’s your ISP, Google, or another public resolver. Most providers keep logs for a limited time to optimize performance and prevent abuse, but these records can also show what websites you visit and when.
That’s why privacy-focused services like Cloudflare and Quad9 promise “no user tracking” and minimal data retention. If you’re serious about online privacy, enabling DNS over HTTPS (DoH) or DNS over TLS (DoT) is highly recommended. Both encrypt your DNS requests, preventing ISPs or network administrators from seeing your browsing history. According to Mozilla, DoH is one of the simplest and most effective ways to protect users from tracking or data interception.
For advanced users, especially those managing multiple accounts through tools like Hidemyacc choosing a secure DNS isn’t just about privacy. It also ensures that each browser profile operates in its own isolated environment, preventing cross-account data leaks and fingerprinting inconsistencies.
7. DNS leaks when using VPN or proxy
A DNS leak happens when your device sends DNS queries outside the encrypted VPN tunnel. In that case, even though your IP is masked, your ISP or visited websites can still see where you’re going. This usually happens when the operating system keeps using your default DNS (often from your ISP) instead of the one provided by your VPN.
You can test your connection using tools like ipfighter.com/dns-leak-check , dnsleaktest.com or ipleak.net. If the results show your ISP’s DNS servers instead of your VPN’s, that means your DNS requests are leaking. To fix it, enable “DNS leak protection” in your VPN app, or manually set your system DNS to Cloudflare, Google, or Quad9.
Some browsers including Chrome and Firefox also support DNS over HTTPS, which adds another encryption layer alongside your VPN. According to Google Developers, many DNS leaks occur when VPN configurations and system DNS settings are out of sync. Flushing your DNS cache after connecting to the VPN or manually overriding the system DNS can usually solve this issue completely.
So, how to prevent it?
The simplest way is to use a VPN that has built-in DNS leak protection. Most modern VPNs automatically route all DNS requests through their own encrypted servers, ensuring that no query escapes the secure tunnel. Always check your VPN’s settings. If there’s an option called Prevent DNS leaks or Custom DNS, make sure it’s turned on.
If you prefer a manual approach, you can set your own DNS servers at the system level. Services like Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) or Quad9 (9.9.9.9) are good choices because they respect privacy and don’t record user activity. This way, even if your VPN disconnects, your device won’t revert to your ISP’s DNS.
Another smart step is to enable DNS encryption directly in your browser. Chrome, Firefox, and Edge now support DNS over HTTPS (DoH) - a feature that hides DNS queries inside encrypted HTTPS traffic. When turned on, even public Wi-Fi providers or network administrators can’t see which websites you visit. According to Mozilla, DoH significantly reduces the chance of DNS data being intercepted or logged.
You should also flush your DNS cache after connecting to a VPN or changing network configurations. This clears any leftover entries from before the secure connection, preventing your system from accidentally resolving domains through the wrong server. On Windows, this can be done by opening Command Prompt and typing ipconfig /flushdns.
8. How to use DNS simply and quickly
Choosing the right DNS Server can improve your internet access speed. Here is a quick guide to changing DNS Server on your computer:
Step 1: Open Control Panel: Click the Start menu and search for "Control Panel."
Step 2: Access network status: Go to "View network status and tasks" to view your network information.
Step 3: Select current network: Select the internet connection you are using.
Step 4: Open Properties: Click the "Properties" button to change network settings.
- Select Internet Protocol Version 4: Find and select "Internet Protocol Version 4" in the list.
- Update DNS: Select "Use the following DNS server addresses" and enter your new DNS address.
Step 5: Click "OK" to save changes. You have completed changing DNS Server and can test your network speed.
- What is Chrome net internals DNS? Clear DNS cache in Chrome
- Troubleshooting DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN on Mobile Devices
- Reduce Ads on All Devices: How Changing Your DNS Can Help
- How to Change DNS on Windows & MAC: A Complete Guide to Improving Your Internet Speed and Privacy
9. FAQ
How do I fix a DNS server problem?
You can reset your DNS settings or switch to a reliable public resolver like Cloudflare or Google DNS. On Windows, run ipconfig /flushdns to clear cached records before reconnecting.
Does DNS improve the Internet?
Yes. A fast and stable DNS improves how quickly websites load and how efficiently your browser resolves domain names.
What happens if DNS is turned off?
Without DNS, browsers cannot translate domain names into IP addresses. You would need to type the numeric IP of every site — which is impractical.
What are the disadvantages of DNS?
Traditional DNS is unencrypted and can be intercepted or logged by ISPs. Also, if a DNS server goes down, websites may appear “offline” even if they’re working.
Does changing DNS bypass all geo-blocks?
No. DNS may bypass lightweight restrictions, but most region locks use IP-based detection. You’ll need a VPN or proxy for full access.
Does DNS over HTTPS slow down queries?
Not significantly. It adds minimal overhead for encryption, but in most modern browsers, the difference is barely noticeable.
Does DNSSEC protect against all spoofing attacks?
It protects against fake DNS responses, but not against network-level hijacking or man-in-the-middle attacks. It’s an important layer, but not a complete shield.
Does a VPN mask DNS queries? (And when does a DNS leak occur?)
A VPN should encrypt DNS queries inside its tunnel, but a leak happens if your system keeps using the ISP’s DNS outside the VPN. Always test your connection after enabling the VPN.
Which resolver should I choose for speed, privacy, or security?
For speed: Google DNS. For privacy: Cloudflare DNS. For security: Quad9 DNS (blocks malicious domains).
How does TTL affect DNS propagation when changing IP or deploying a website?
TTL (Time to Live) determines how long DNS records are cached. Lower TTL values make changes propagate faster, which is useful when moving servers or updating records.






